Toolkit for Innovative and Eco-Sustainable Renovation process
The Toolkit for Innovative and Eco-sustainable Renovation Processes has been developed in the framework of the Med-EcoSure project – Mediterranean University as catalyst for Eco-Sustainable Renovation, by the research group beXLab (building environmental eXperience) at the DIDA Department of Architecture of the University of Florence.
The Toolkit proposes an innovative, interactive, bottom up and participative programme of training and education for technicians and students within a Living Lab environment, with a list of suggestions for the renovation of Mediterranean public buildings.

The toolkitfor Innovation and Eco-Sustainable Renovation processes is a box composed by:
1. The toolkit
2. The Abacus
3. The Best Practices

1. The Toolkit
The Toolkit is a guide to innovate the retrofit process of university buildings in the Mediterranean area with information, procedures, tools and tips to create energy efficient, eco-sustainable, comfortable and beautiful future public buildings.
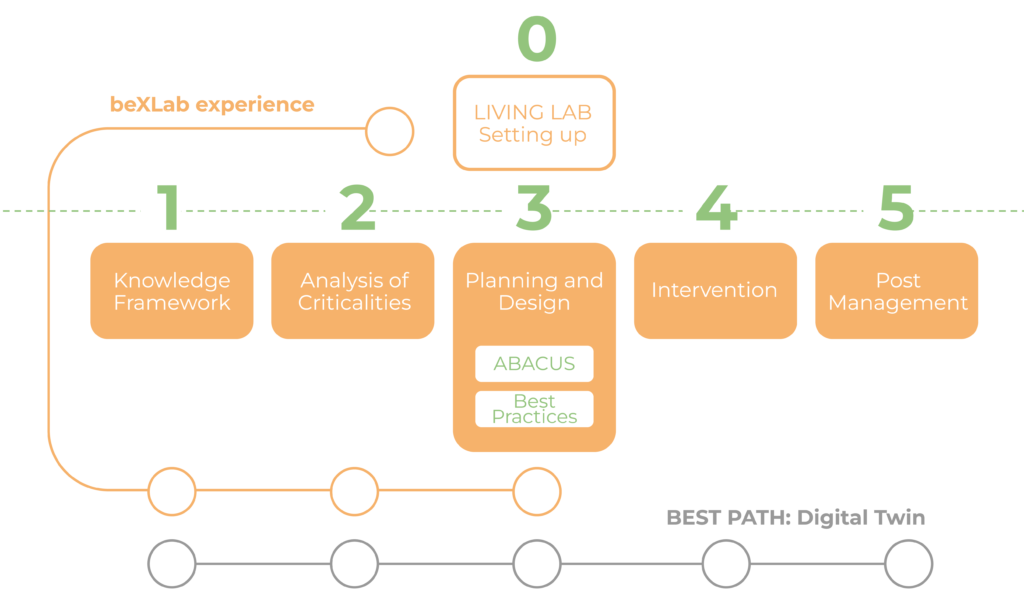
It is structured to explain step by step how to approach the retrofit of university buildings stocks as an innovative process built around the role of people, as decision makers, stakeholders and users gravitating around the university building.
The structure of the Toolkit is organized in six sequential phases encompassing the whole renovation process, from the initialization of a Living Lab that supports innovative renovation processes, to the management of the renovated building.
Within the document two sessions proceed in parallel with the progression of renovation phases:
the BEST PATH: Digital Twin implementation to innovate the renovation process;
the beXLab experience, as an example of application of the Toolkit in the real-case pilot inside the University of Florence.
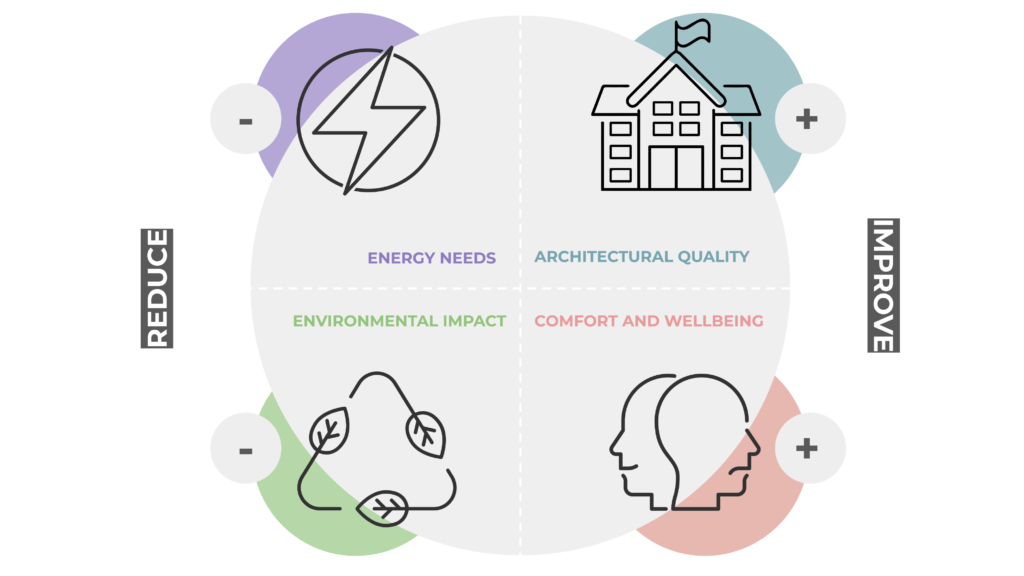
The toolkit is intended to guide the renovation process towards the achievement of four overarching renovation objectives:
Architectural quality: renovation is the occasion for an aesthetical requalification of existing buildings, contributing to the definition of a new image, speaking of sustainability;
Energy efficiency: renovations strive at first instance for the reduction of the building’s energy needs, so that the low energy demand can be fully satisfied by renewable energy;
Comfort and Wellbeing: renovations improve the indoor environmental quality of existing living spaces, contributing to occupants’ comfort, wellbeing and health;
Environmental impact: ambitious renovations minimise the carbon footprint of buildings, reduce the environmental impact of existing buildings.
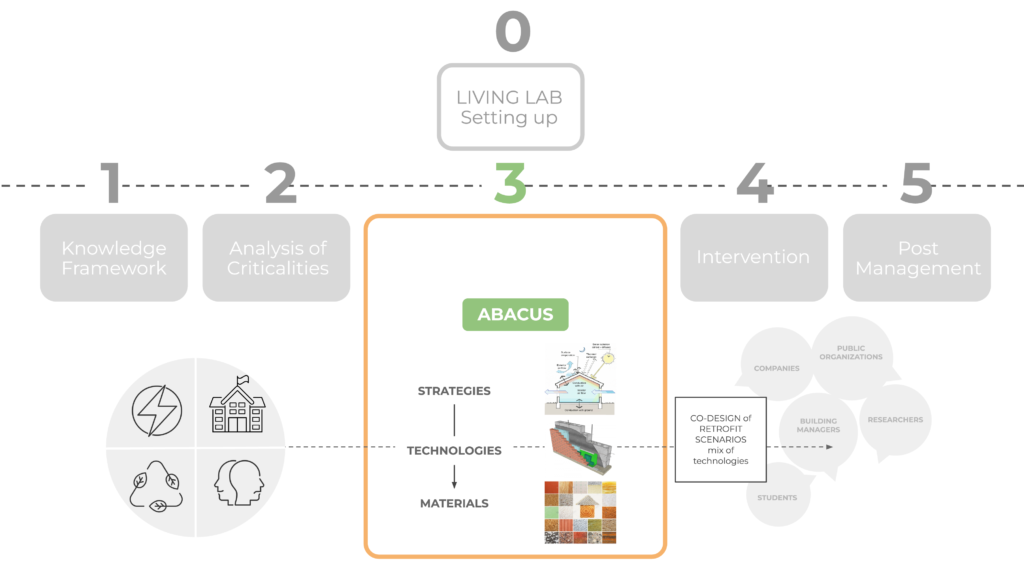
2. The Abacus of Retrofit Design
The Abacus is an organised and navigable selection of strategies for building retrofits in the Med socio-climatic context, correlated with appropriate technologies and materials. Dedicated to high educational/university building, the Abacus can also inform the pre-design phase of public buildings’ renovation, insipiring the first phases of co-design.
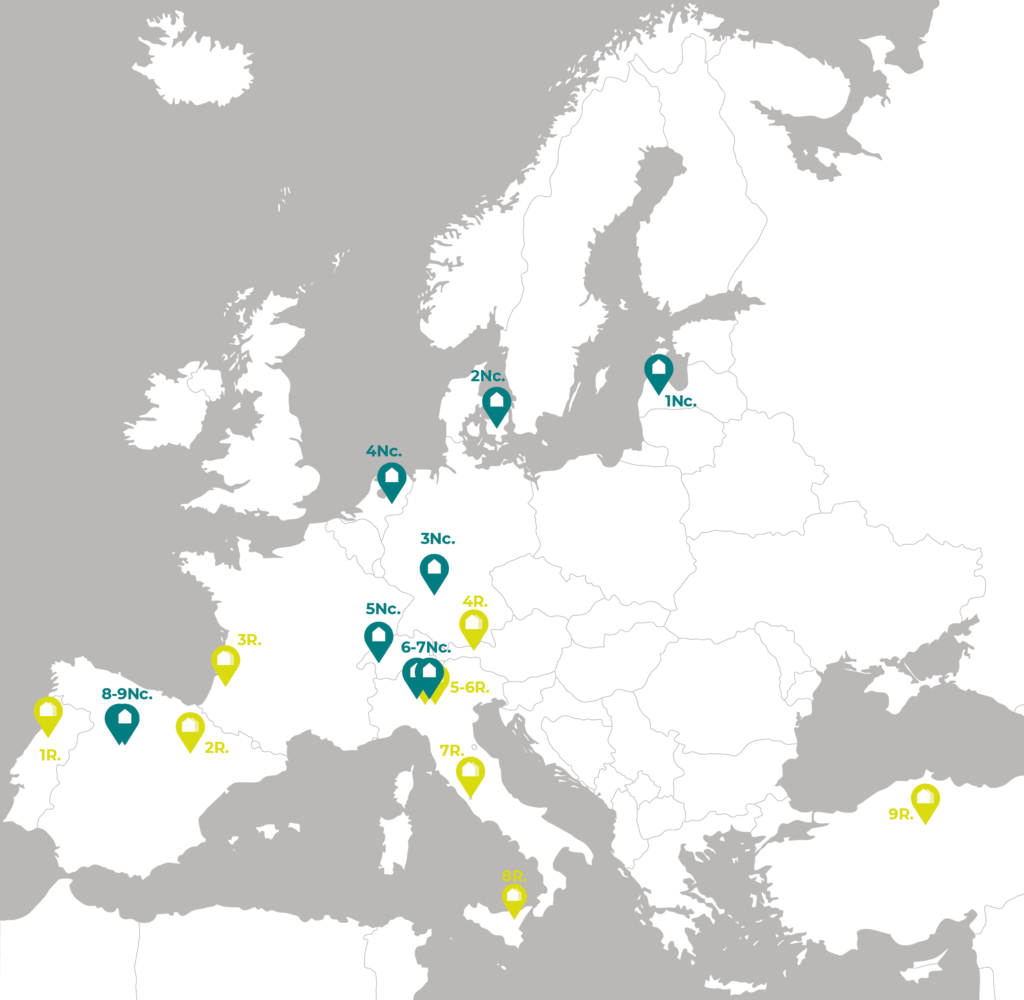
3. The Best Practices
The research collected, analysed and catalogued a total of 18 case studies, concerning 9 new university complexes and 9 cases of energy renovation of existing high educational buildings.
Considering both qualitative and quantitative data, a set of indicators has been defined as basis for the evaluation of the case studies, which allowed the definition of a base-line for the subsequent comparison between them.
The Toolkit, the Abacus, and the Best Practices documents follow a defined sheet layout in standard format (.ppt/.pptx), in order to allow users to extend the contents with new examples, case studies, strategies, materials, and local experiences, and to enrich the Mediterranean path towards innovative and eco-sustainable renovation practices.


